Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas
Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas are a type of cancer that impacts the lymphatic system.
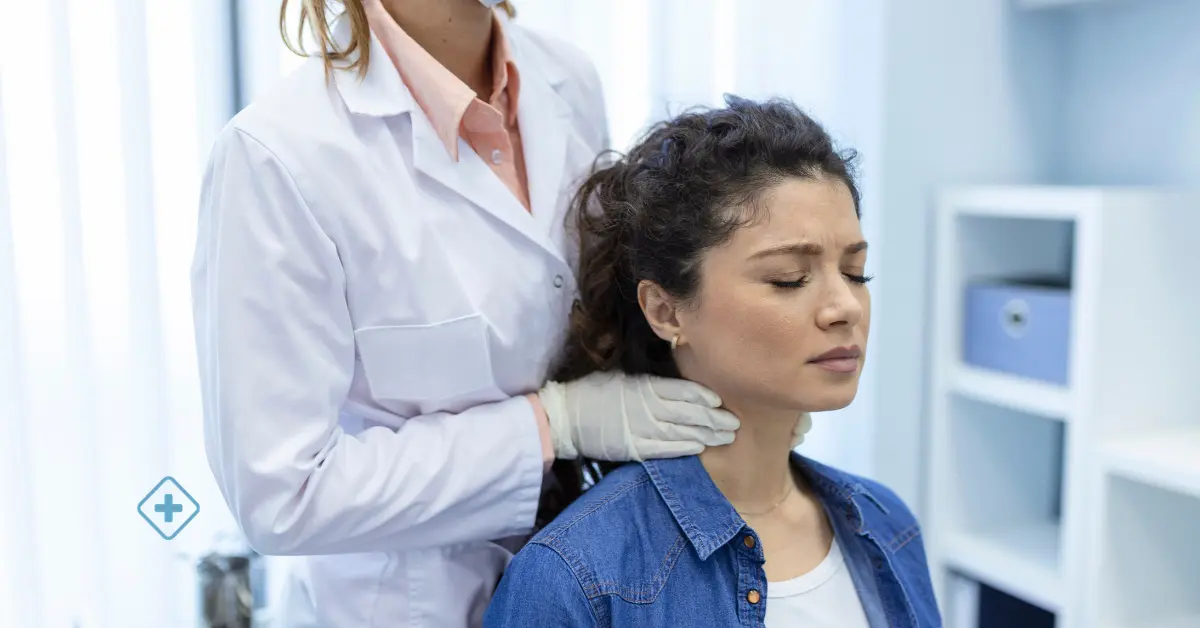
Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (also known as lymphoma or NHL) are a type of cancer that impacts the lymphatic system, a part of your body's immune system. They start when lymphatic cells become malignant and start to grow and divide in an uncontrolled manner. Oncologists and Hematologists are the main specialists in this condition.
These abnormal cells can gather in the lymph nodes, but they can also spread to other parts of the body such as the bone marrow, spleen, liver, and other organs.
Unlike Hodgkin lymphomas, NHLs do not have specific cells known as Reed-Sternberg cells. These lymphomas develop from lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, and can affect people of all ages.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms can be different depending on the specific type and location of the lymphoma. Some of the common symptoms include:
-
Swollen lymph nodes, in your neck, armpits, or groin
-
Persistent fever without a specific cause
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Excessive night sweats
-
Constant fatigue
-
Itchy skin
-
Abdominal swelling or pain
-
Chest pain, cough, or difficulty breathing
It's important to note that these symptoms can be similar to those of other diseases, thus it's vital to get a proper medical diagnosis.
How many types of Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas exist?
The lymphoma type is based on the affected lymphocyte type (B or T cells), the stage of maturity of these cells when they become cancerous, and other factors. There are two main types of lymphocytes in the lymphatic system:
-
B Lymphocytes (B cells): These normal B cells help protect the body against infections by producing antibodies, proteins that latch onto germs and tag them to be destroyed by other components of the immune system.
-
T Lymphocytes (T cells): There are different types of T cells. Some destroy germs or abnormal cells in the body while others regulate the activity of other immune system cells.
The lymphoma can start in any lymphocyte type, but B cell lymphomas are more common. Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas can also be classified as indolent lymphomas or aggressive lymphomas based on their growth and spread rate:
-
Indolent lymphomas: Grow and spread slowly. Some indolent lymphomas don't require immediate treatment and can be closely monitored. Follicular lymphoma is the most common indolent lymphoma type in the United States.
-
Aggressive lymphomas: Grow and spread quickly and usually require immediate treatment. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common aggressive lymphoma type in the United States.
It's important to note that some lymphoma types, such as Mantle cell lymphoma, don't clearly fit into these categories.
Regardless of the growth rate, all Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas can spread to other parts of the lymphatic system if untreated, and can also disseminate to other parts of the body like the liver, brain, or bone marrow.
The most recent classification is by the World Health Organization (WHO), which groups lymphomas according to the origin lymphocyte type, the lymphoma's microscopic appearance, the chromosomal characteristics of lymphoma cells, and the presence of certain proteins on the surface of the cancerous cells.
How are lymphomas diagnosed?
Diagnosing Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas generally involves a combination of tests and procedures that your Oncologist and Hematologist could recommend.
This may include blood tests to look for signs of inflammation or abnormalities in blood cell levels, lymph node or affected tissue biopsies to examine cancerous cells, as well as diagnostic imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs to determine the location and the cancer extension.
What are the risk factors?
Some of the risk factors may increase the chances of developing Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. These include:
-
Medications that suppress the immune system
-
Having a weakened immune system
-
Family history of the disease
-
Chronic viral infections (such as Epstein-Barr virus or human T-cell lymphoma virus)
-
Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation
How to prevent Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas?
There is no way to prevent Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of developing any type of cancer in general. This includes following a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and not smoking.
If you suspect that you or someone close may be facing Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, it's crucial to seek specialized medical attention. At BlueNetHospitals, we strive to provide the highest level of oncological and hematological care, a compassionate attention and a focus on the well-being of our patients and their families.
BlueNetHospitals
BlueNet Hospitals - Blue Net Hospitals

Hematomas
Hematomas can occur for a variety of reasons, with injuries and trauma being the most common
Leukemia
Leukemia cannot be completely prevented, but there are measures that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing it.
Anemia
Anemia often results in a weak condition and a feeling of tiredness. Anemia is characterized by an abnormally low number of healthy red blood cells in the blood. Red blood cells that carry oxygen around in your organism.
- Do You Need an Appointment with a Specialist?
- call us
- write us
- let's talk