10 Most Popular Epilepsy Myths
These are some of the most repeated myths about this Neurological disorder
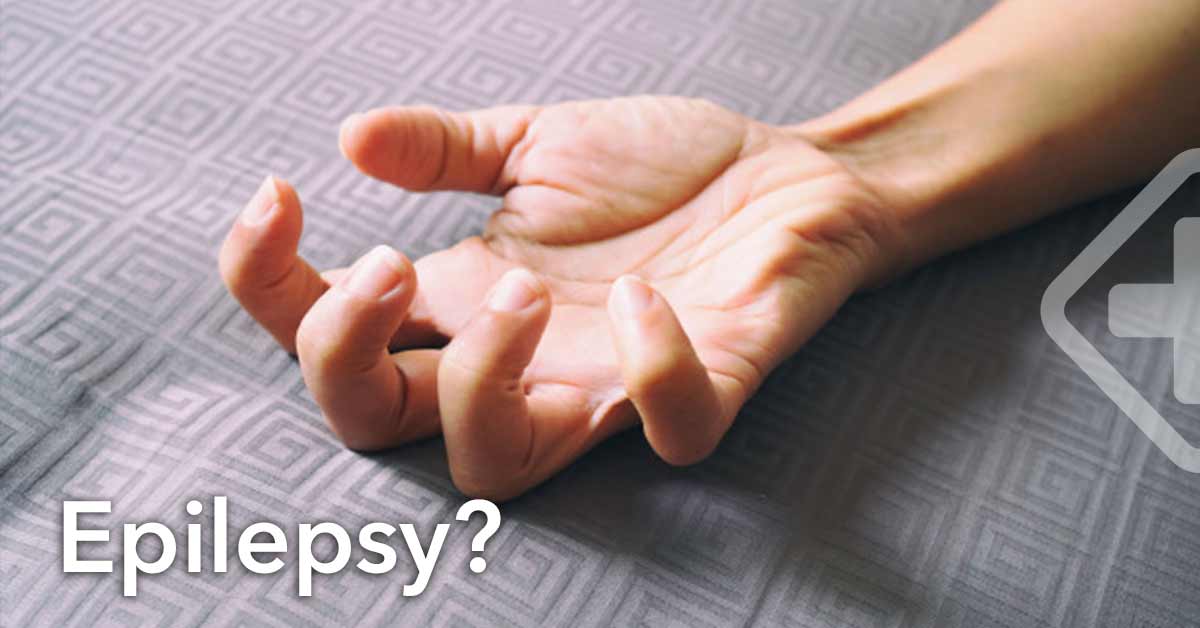

Epilepsy is one of the most common Neurological disorders affecting more than 50 million people worldwide. This non-communicable brain disease occurs when neurons send wrong signals causing seizures or unusual behavior in people who have it.
Epilepsy can develop in anyone, men or women, of any age, and it is estimated that approximately 4 out of every 1000 people in the world have Epilepsy.
Many statements and prejudices surrounding this disease have gradually become popular and are far removed from reality and may unnecessarily stigmatize the patient that suffers from this disorder.
Myths About Epilepsy:
Myth #1: If you've ever had a seizure it means you have Epilepsy
Fact: A person is diagnosed with Epilepsy when they have 2 or more unprovoked ("out of the blue") seizures that occur more than 24 hours apart. But when something causes a seizure, such as excessive alcohol consumption, lack of sleep, or a new medication, these are not related to Epilepsy. Also, there are non-seizure Epilepsy episodes.
Myth #2: During a seizure, a person can swallow or choke on the tongue
Truth: It's not like that. During more intense seizures, a person may bite their tongue, but nothing serious can happen; however, trying to force open the mouth of a person having a seizure can cause lacerations on the lips or gums.
Myth #3: You must force something into the mouth of someone who is having a seizure
Truth: Under no circumstances should you put anything in a person's mouth if they have a seizure. This could seriously injure them. Turn the person on his or her side, keep a safe distance from nearby objects, and let the seizure run its course. If you see signs of distress or if the seizure continues for more than a couple of minutes, call 624 1043-911 immediately.
Myth #4: People with Epilepsy are mentally ill or emotionally unstable
Truth: Epilepsy is a general term that covers many types of seizures and epileptic disorders. It is a functional problem, physical, not mental, and has many unidentifiable causes.
Myth #5: People with Epilepsy are not as smart as other people
Fact: False. Epilepsy has little or no effect on a person's ability to think, except during some seizures, for a short period after some seizures, and sometimes as a side effect of certain antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsy is not synonymous for mental difficulties because there is not necessarily brain damage.
Myth #6: People with seizures can't handle demanding, high-pressure jobs
Truth: They often can, and do. Most professions, including those at the highest levels of business, government, the justice system, sports, and medicine, can accommodate a person with Epilepsy.
Myth #7: It's easy to tell when a seizure is about to occur
Truth: It is not yet possible to predict when seizures will begin, although some patients say they may feel a brief sensation within seconds of a seizure.
Myth#8: Seizures are painful
Truth: A person is unconscious and feels no pain during most seizures. When the seizure is over, the patient will probably feel discomfort or muscle pain if he/she fell orbit his/her tongue during the seizure.
Myth #9: Epilepsy is Contagious
Truth: Different causes have been related to Epilepsy, however, in more than 70% of the people who suffer from it, the cause has not been identified, and the contagion. What is clear is that through contagion, it is not transmissible.
Myth #10: Epilepsy cannot be effectively controlled
Truth: There are many ways to treat Epilepsy. With antiepileptic drugs, it is possible to control seizures in almost 70% of patients adequately.
Remember that the first source of reliable information is your Doctor. Consult your Neurologist if you have more questions about Epilepsy.
Trending Topics
Gestational Diabetes
The exact cause of gestational diabetes is not yet fully understood.
E. coli
The symptoms of an E. coli infection can appear three to four days after exposure
Diabetic Foot
These are the common symptoms related to diabetic foot
Hip Dysplasia
The symptoms of hip dysplasia vary depending on the individual's age
Health Library
Neurology
Learn More About:
- Do You Need an Appointment with a Specialist?
- call us
- write us
- let's talk